The following sections cover the finer technical details of the improvements in the JavaScript SDK v1.1 that make it more efficient and easier to use.
Sending events using Beacon
The JavaScript SDK v1.1 lets you send the event payloads using the XHR (XMLHttpRequest) API (default) or Beacon browser utility.
The Beacon browser utility asynchronously sends a small amount of data over HTTP to the RudderStack server. To send the SDK events using this utility, set the useBeacon field in the load() call options to true.
sendBeacon version of the JavaScript SDK located here and its XMLHTTP version located here are no longer supported.The JavaScript SDK internally uses a separate queue (BeaconQueueOpts) to hold the data and send it through the Beacon utility in batches. The structure of BeaconQueueOpts is shown below:
{ maxItems: 10 flushQueueInterval: 600000}The following table describes the above integer type parameters in detail:
| Parameter | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
maxItems | The SDK flushes the queue when the default number of payloads is reached. | 10 |
flushQueueInterval | The SDK flushes the queue after the default time interval (in milliseconds) is reached. | 600000 |
maxItems or flushQueueInterval values.Advantages
There are two key advantages of using the Beacon utility to send your event payload:
- Pushing events to the Beacon queue is faster than the XHR instrumentation, so there are some performance improvements in the JavaScript SDK.
- The Beacon requests are optimized so that the browser waits until the CPU load is lower or until the network is free before making the actual requests, leading to better website performance.
Event delivery and retry mechanism
This section highlights some important points which will help you choose whether to use Beacon for sending your event payloads:
- The requests sent from the SDK using the Beacon utility only push the events to the browser's Beacon queue. Further, it depends on the browser's engine to send these events from the queue. Hence, RudderStack does not guarantee if any events get discarded due to any 5xx or other network-related errors (request timed out, end resource unavailable, etc.).
- The Beacon queue maintained by the browsers limits the total size of the elements present in the queue at any point and peaks at 64 KB. Therefore, you cannot send high-frequency hits from the main thread in one go, as the Beacon queue cannot take up cycles to dequeue itself. The JavaScript SDK handles this by maintaining a separate queue that retries pushing events to the Beacon queue if they are not successfully pushed in the first attempt.
Reduced core SDK size
As RudderStack supports more native destinations through the JavaScript SDK, more instrumentation code is likely to be added to it. This increases the SDK size and requires the browser to evaluate and parse more unused JavaScript.
Therefore, these instrumentation codes will not be bundled for the end destinations in the core JavaScript SDK. Instead, the SDK will only fetch the destination configuration settings from the RudderStack dashboard, such as track ID, API key, secret, etc., using the requireIntegration method.
requireIntegration call definition
The requireIntegration method contains the following two parameters:
- The first parameter is a string or an array of strings containing the destination names.
rudderanalytics.requireIntegration(“All”). This will fetch the plugins for all the native destinations connected to your source in the RudderStack dashboard.- The second parameter is a callback that accepts an object containing the names of the destinations successfully or unsuccessfully loaded on the page.
An example is shown below:
rudderanalytics.requireIntegration( ["GoogleAnalytics", "Hotjar", "Hubspot"], function(object) { console.log(JSON.stringify(object)); });How it works
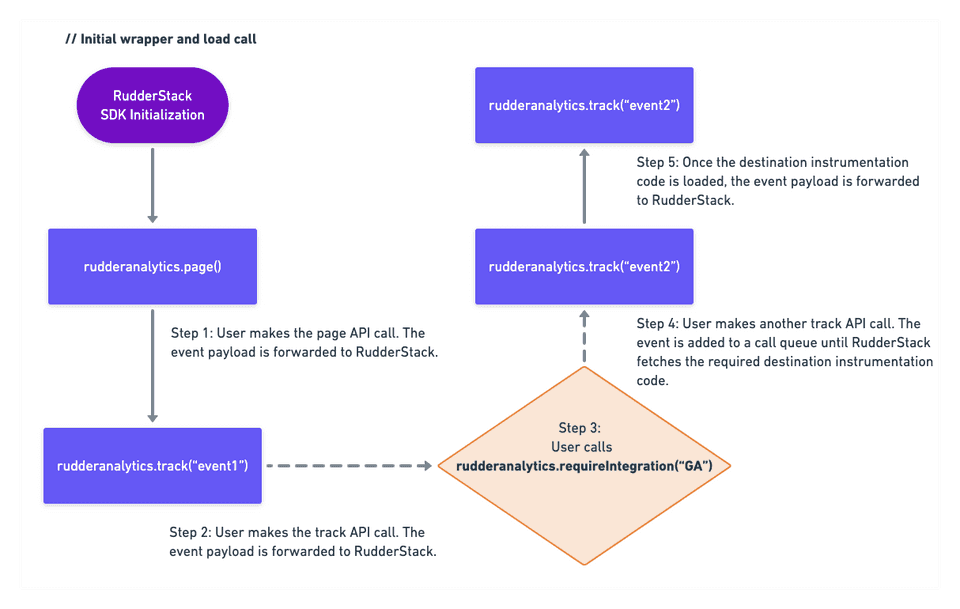
Once the JavaScript SDK receives a requireIntegration call, for example, rudderanalytics.requireIntegration("GA"), it automatically fetches the Google Analytics instrumentation code (GAPlugin.js).
The SDK maintains a call queue, and the API calls are processed one after the other. The SDK blocks the processing of this call queue once you call the requireIntegration method.
Use-case
Suppose the user makes a call rudderanalytics.requireIntegration("GA"). All the subsequent calls made to the SDK (such as page, track, alias, group, etc.) will get enqueued until the GAPlugin.js and Google Analytics' analytics.js is loaded on the web page. Once the plugin and the end destination snippet is loaded, the calls in the queue will be processed, and the corresponding calls to analytics.js will start flowing.
trackingId and other configuration settings are fetched from the RudderStack dashboard and the SDK is configured using these settings.Sample call flow
The following workflow sums up the flow of the event payload when the user calls requireIntegration():
Contact us
For more information on the topics covered on this page, email us or start a conversation in our Slack community.